Damp Proof Course (DPC)
BNi Building News. Part 3 - 2016. (888) 264-2665. Building standards that have been adopted by state agencies without change from building standards contained in national model codes; Building standards that have been adopted and adapted from national model codes to address California's ever-changing conditions; and. Building standards.
Type B Vertical DPC NBS Source
The thickness of DPC is not a mere detail; it is a crucial factor influencing its effectiveness. Compliance with building regulations and considerations of environmental conditions guide this decision.. (DPC) in a building is a crucial construction element designed to prevent the capillary rise of moisture through walls, providing a barrier.

How to lay a DPC YouTube
Function ~ the primary function of any damp-proof course (dpc) or damp-proof membrane (dpm) is to provide an impermeable barrier to the passage of moisture. The three basic ways in which damp-proof courses are used is to:-. Building Regulations, Approved Document C2, Section 5: A wall may be built with a damp-proof course of bituminous.
Building Guidelines Cavity walls DPC's
A Damp Proof Course (DPC) is a continuous barrier installed in buildings to prevent capillary climb of water in walls. Current building regulations state that walls must resist the passage of water from the ground and that this requirement can be reached if a damp proof course is provided. Therefore almost all modern houses within the UK will.
D.P.C., D.P.M. and Cavity Tray Road To Learning
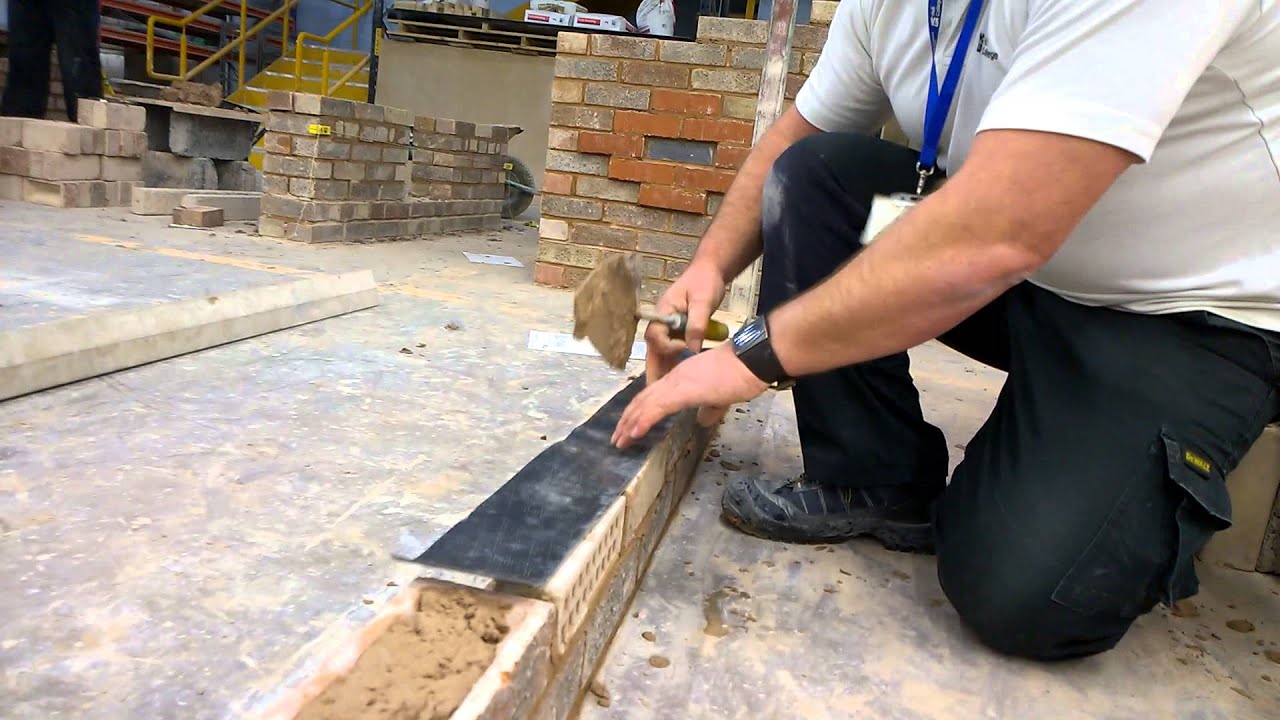
8 handy hints for installing horizontal damp proof course. The inner leaf damp proof course must link with the upstand to the damp proof membrane, by a minimum of 50mm and be sealed to it. This is to ensure a continuous barrier against damp, this includes where low level cills are present ie doorways. Lay the DPC on a full even bed of fresh.

Damp Proof Course (DPC) Methods of DPC application in Construction Cement Concrete
Numerous lintels also act as a DPC but where these are less than 150mm in height (commonly many are 140mm) they do not technically satisfy the damp protection requirements demanded in Building Regulations Part C and British Standards unless accompanied with additional DPC protection providing the minimum dimension stipulated. PRODUCT NNAME--GGROUP

Damp Proof Course (DPC) Methods of DPC application in Construction Cement Concrete
DPCs are now required to construct new buildings, preventing rising/penetrating damp which can lead to costly repairs due to mould and damp in the building materials.

All About Damp Proof Courses (2022)
A damp-proof course is a barrier, usually formed by a membrane, built into the walls of a property, typically 150 mm above ground level, to prevent damp rising through the walls. Historically, damp-proof courses may have been formed using bitumen, slates, lead, pitch, asphalt or low absorption bricks. They emerged during the Victorian era and.

Damp Proof Course (DPC) Methods of DPC application in Construction Cement Concrete
A metal damp proof course (DPC) between the stone foundation and brick wall. Damp proofing in construction is a type of moisture control applied to building walls and floors to prevent moisture from passing into the interior spaces. Dampness problems are among the most frequent problems encountered in residences. DPC visible between concrete foundation and brickwork.

What is DPC Damp Proof Course? DPC Material and Detailed Information Civil Site
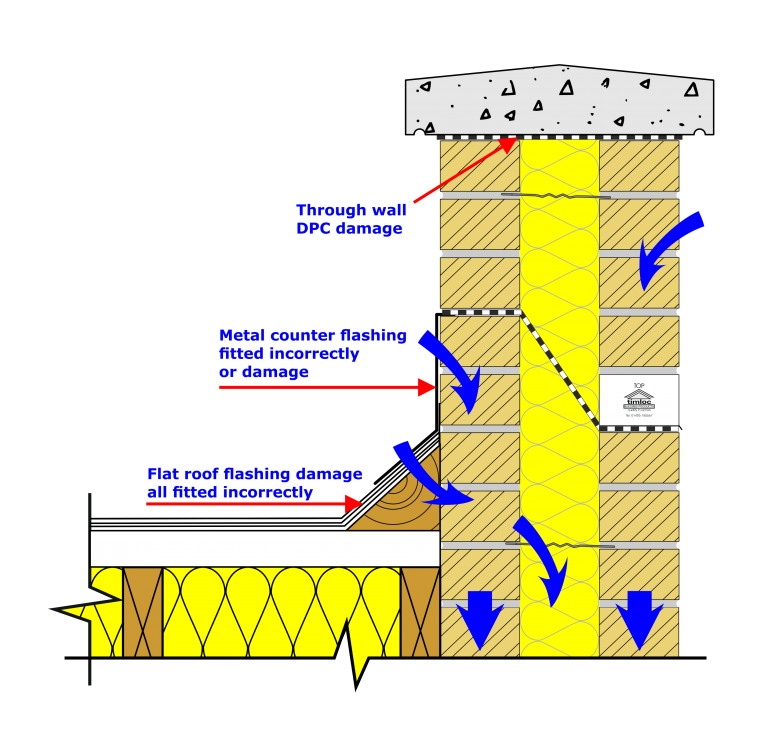
In all cases, cover flashings should be built-in under the stepped DPC. Metal used for flashings should be non-ferrous. In cases where lead is used, the lead should be at least a code four (colour code blue). Laps for flashings should be greater than 100 mm (150 mm in locations prone to high wind and rain) and individual lengths should be less.
Building Guidelines Cavity walls DPC's
Now effective! 2022 California Building Standards Code, Title 24, California Code of Regulations. Effective January 1, 2023 to December 31, 2025. It's that time again! The 2022 edition of Title 24 is now available. Publication date: July 1, 2022. Effective date: January 1, 2023. See the Codes tab for more information.

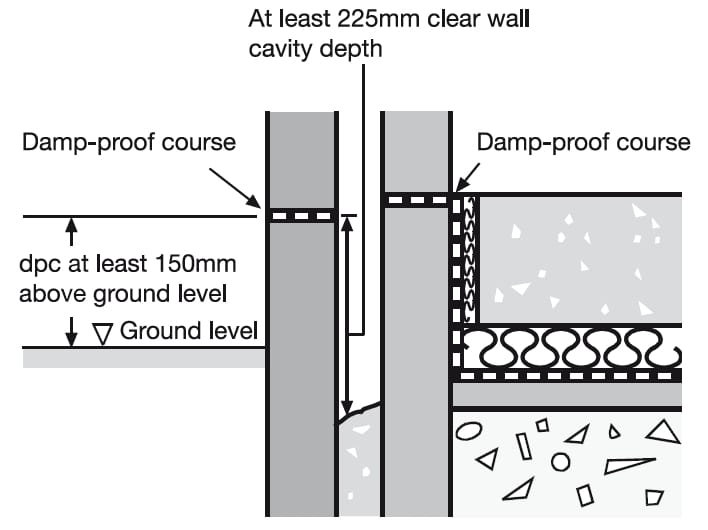
6.1.17 DPCs and cavity trays NHBC Standards 2020 NHBC Standards 2020
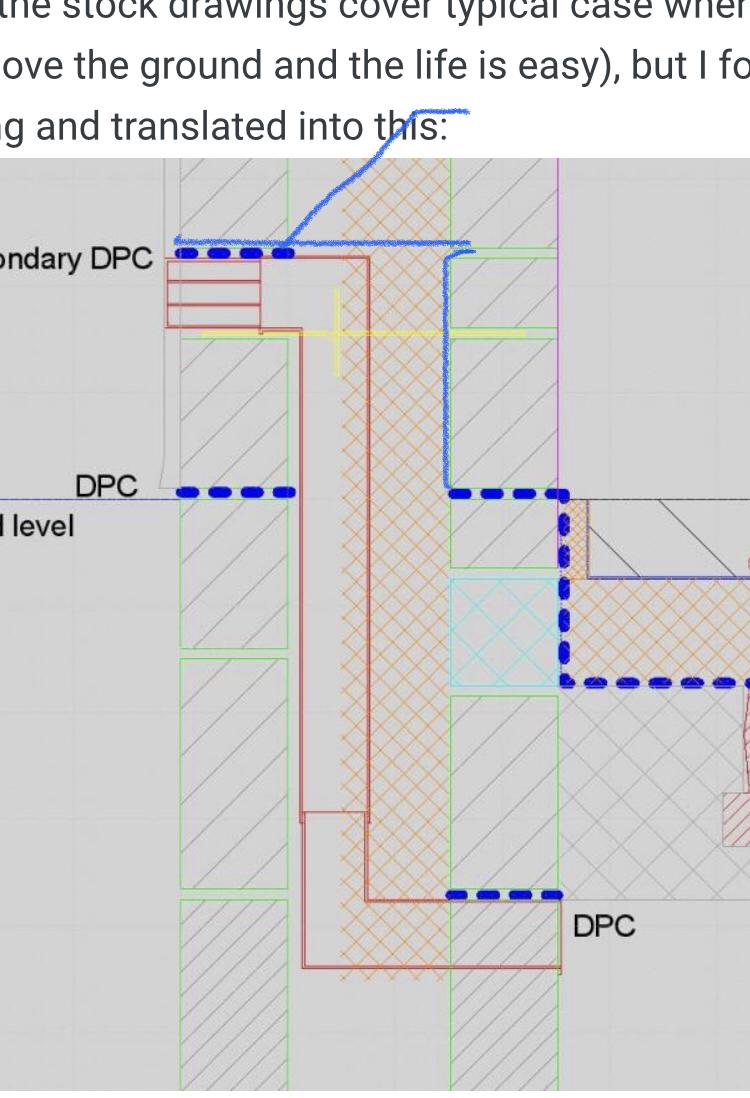
impermeable. Figure 9: DPC at least 150mm above finished ground level Figure 10: Stepped DPC levels on sloping sites Where homes are 'stepped' on a sloping site, care should be taken to link DPCs and DPMs so that all parts of each home are protected. DPC materials # Acceptable materials for DPCs include:
Building Guidelines Cavity walls DPC's
DPC barriers are required when constructing new buildings to prevent rising damp, and in some cases, it can also help prevent penetrating damp or water ingress. There are different regulations for walls and floors, as these face different risks and causes of damp - rising damp as well as penetrating damp and condensation must be protected against.

Damp Proof Course (DPC) Methods of DPC application in Construction Cement Concrete
User note: About this chapter: Chapter 3 contains a wide array of building planning requirements that are critical to designing a safe and usable building. This includes, but is not limited to, requirements related to: general structural design, fire-resistant construction, light, ventilation, sanitation, plumbing fixture clearances, minimum room area and ceiling height, safety glazing, means.

Damp Proof Course (DPC) Methods of DPC application in Construction Cement Concrete
A cavity wall is designed to prevent moisture penetrating to the inside face of the wall and causing damp problems in the building. In many situations it is necessary to include cavity trays in the wall, to prevent water penetration to the inner leaf.
FFL at ground level Damp & DPCs
14.10.2021 News Cavity trays are an important feature in external cavity walls to assist in ensuring any water is directed outside the building. Incorrect specification or installation can lead to defects in the wall and water damage that might be expensive or needlessly destructive to rectify.